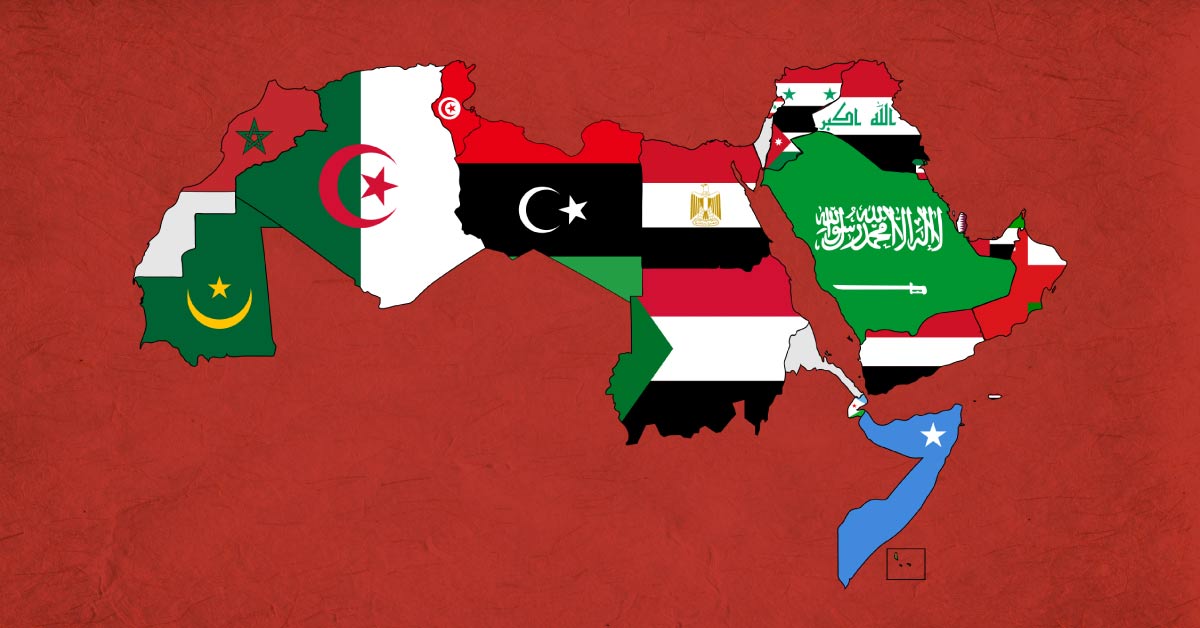
Arabic speaking Countries

The majority of Arabic-speaking countries are concentrated in the Middle East and North Africa, or what we call today the Arab world. The number of countries that consider Arabic an official language or a common official language reaches 25 countries. The most populous is Egypt, which has a population of 100 million, and more than 93 percent of its total population speaks Arabic as a mother tongue
History of the Arabic language
Arabic is one of the most widely spoken languages in the world, and it falls under the Middle Semitic language family that includes Aramaic, Hebrew and Phoenician.
The Arabic language is the daughter of the desert. The Bedouins transferred it in their
travels from one region to another, until it spread in a number of Arabic-speaking
countries.
In the seventh century AD, the Arabic language spread with the Islamic conquests that extended across the Middle East, North Africa, Central and Western Asia, and into areas in China. The presence of the Arabs who carried their language, religion and culture with them in different parts of the world played a major role in planting the seed of the Arabic language, which grew with the passage of time.
Today, Arabic speakers use colloquial dialects of up to 30 dialects. While Modern Standard
Arabic is taught in school curricula and used in the media and workplaces, all literary texts composed between the seventh and ninth centuries AD were written in Standard Arabic, in addition to being the language of the Holy Qur’an.